- Insolvency is a state when an individual, corporation, or other organization cannot meet its financial obligations for paying debts as they become due.it is also where debtors can't meet.
- Technically, bankruptcy occurs when a court has determined insolvency, and given legal orders for it to be resolved.
- Bankruptcy is a determination of insolvency made by a court of law with resulting legal orders intended to resolve the insolvency by paying off debts.
HISTORICAL BACKGROUND
- originated in English law
- earliest insolvency legislation can be traced to sections 23 and 24 of the Government of India Act, 1800 (39 and 40 Geo III c 79), which conferred insolvency jurisdiction on the Supreme Court.
- especially Statute 9 in 1828
- first insolvency act-1848 and provincial Insolvency Act,1920
- Under the Constitution of India ‘Bankruptcy and Insolvency’ is provided in Entry 9 list Concurrent list, (Article 246 – Seventh Schedule to the Constitution) i.e. both Center and State Governments can make laws relating to this subject.
- improving the allocative efficiency and getting them at par with international standards along with incentivising foreign investors.
- headed by Justice V.B. Eradi for changes in existing laws including avoiding delays and encouraging transparency.
- quick asset disposal
- possibilities of revival/rehabilitation
- urgent need of streamlined laws and processes
- jurisdiction,power and authority vested in NCLT instead of High court
- insolvency professionals from recognised institutions
- brought out the dismal time taken to wind up a company in India – which ran on an average upto 25 years.
N L MITRA ADVISORY GROUP (2001)
- examined conflicts on justice tribunalisation of common law and civil law.
- under article 323 in India
- not possible to oust the jurisdiction of the High Court under Articles 226 and 227 without amending the provision of Article 323B.
- possibility of avoiding duality and adopting alignment.
J J IRANI COMMITTEE (2005)
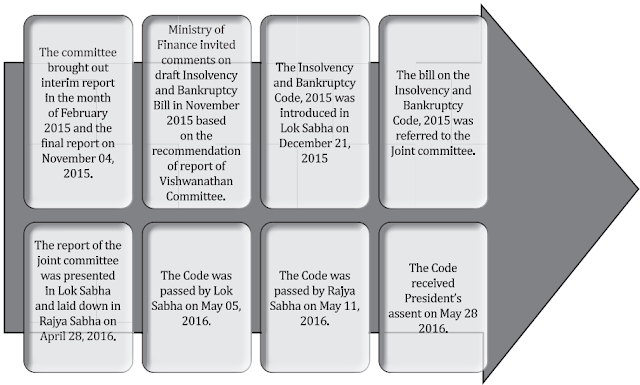
- 02/12/2004 submitted report in 05/2005 for simplified compact law to address changes and provide flexibility.
BANKRUPTCY LAW REFORMS COMMITTEE (2014)
- entrepreneur friendly for SMEs for easy exit
- set up under Shri TK viswanathan on 22/08/2014
- objectives of the Committee were to resolve insolvency with: lesser time involved, lesser loss in recovery, and higher levels of debt financing.
- consolidation of existing legal framework
- establish creditors committee to come up with revival/repayment plan
- outlined insolvency resolution procedures initiated by dr./cr.
- proposed that operational creditors be allowed to initiate IRP
- managed by licensed insolvency professional for controlling/managing assets
- proposed to set up insolvency professional agencies for admitting members and developing code of conduct
- 180 days for IRP completion and extended by 90 days if 75% creditors agree
- establish info utilities
- proposing to establish IBBI as regulator
- proposing NCLT/DRT for insolvency resolution
highlights of IBC,2016 w.r.t corporate insolvency
- preamble reads
- to consolidate/amend laws
- time bound
- maximization of asset value
- promote entrepreneurship
- credit availability and balancing interests
- appeals against NCLT shall lie before NCLAT and appeals against DRT lied before DRAT
- proposes to established an insolvency regulator (the Insolvency and Bankruptcy Board of India) to exercise regulatory oversight over
- ― Insolvency Professionals,
- ― Insolvency Professional Agencies (develop standards,ethics code and exercise a disciplinary role) and
- ― Information Utilities (gather info and form databases for status checks)
- swift timeline of 180 days with one-time extension of 90 days and mandatory completion within 330 days from insolvency commencement including extensions plus legal proceedings.
- resolution plan approved by 66% of voting share of financial creditors along with adjucating authority's sanction.
- if said plan rejected, AA issues liquidation order
- lays down fast track insolvency resolution process within 90 days extended upto 45 days provided 75% financial creditors agree.
THE INSOLVENCY AND BANKRUPTCY CODE 2016 - AN INTERNATIONAL COMPARISON WITH REFERENCE TO CORPORATE INSOLVENCY RESOLUTION PROCESS
- INSOLVENCY PROOF
- IBC (SEC. 4)
- min. default amount=1 Lakh increased by govt. through notification upto 1 crore.
- US
- no proof required
- UK
- doubtful solvency=indication of financial hurdles and whether rehabilitation needed
- administration order made when
- unable to pay debts OR likely to become unable to pay debts
- reasonably likely to achieve administration
- UNSECURE CREDITORS
- IBC (SEC. 8&9)
- can initiate resolution process (IRP) after giving 10 days demand notice
- US
- same as IBC
- Chapter 11 proceeding commenced after a petition filed by 3/more entities who is
- a non-contingent,undisputed claimholder;which is atleast $10,000 more than lien on debtor's property
- an indenture trustee
- UK
- any creditor may apply for administration order
- MORATORIUM
- IBC (SEC. 13,14&31)
- NCLT may declare starting from app acceptance till resolution plan approval
- many countries provide automatic moratorium with suitable safeguards
- US
- Sec. 362 of US Bankruptcy code provides automatic on claim enforcement upon filing ch 11 petition
- covers
- judicial/administrative proceedings
- judgement enforcement
- acts obtaining possession/control
- create/perfect/enforce liens
- collect claim
- exercise set off rights
- tax court proceedings
- secured creditors may apply to lift stay
- stay lifted if debtor has not adequately protected property interests
- UK
- Schedule B1 of IA 1986
- interim moratorium between application/intention to appoint and actual appointment
- broad automatic moratorium
- automatically on security enforcement and can be lifted with court/administrator approval
- automatic+interim to prevent creditor race
- RESOLUTION PROFESSIONAL (RP) APPOINTMENT
- IBC (SEC 16&22)
- Interim RP appointed by NCLT within 14 days from insolvency commencement and such appointed as RP if 66% financial creditors agree.
- US
- court passes appointment order of trustee only when subject to any fraud, dishonesty, incompetence, gross mismanagement or where such an appointment will be in the interest of creditors, any equity security holders, and other interests of the estate.
- UK
- holder of qualifying floating charge (QFC) having substantial stake may appoint to act early by filing following documents:
- appointment notice: statutory notice from appointer of reliable QFC
- administrator consent
- others as prescribed
- MGMT. TAKEOVER AND RP DUTIES
- IBC (SEC. 17,18&25)
- takes custody/control of all assets
- UK
- administrator plays central role in rescue process and has power to do anything necessary;power to carry on business
- co./officer can;t exercise mgmt. powers without administrator consent
- court's power to direct administrator limited to whether all proposals rejected in creditors meeting or if change in circumstances needed.
- administrator can remove/appoint director
- entry into administration doesn't terminate BoD if administrator permits such as mgmt. has to cooperate with administrator under Section 235 of IA 1986
- US
- debtor-in-possession regime
- mgmt. encouraged to make timely reference and wouldn't fear control loss
- criticized as leaves the people responsible in charge and increases possibility of fraud but safeguard in form of trustee acting as an agent to all parties under Sec.1104
- appointed by the court on the request of an interested party or the trustee at any point of time after the commencement of Chapter 11 proceedings but before a plan has been confirmed
- considered an extraordinary remedy and requires a high standard of proof
- court has no discretion once sufficient cause for appointment found
- EXAMPLE:CELERITAS TECHNOLOGIES
- While appointing a trustee under Section 1104(a)(2) in the best interests of the creditors, the court has held that the debtor’s ability to fulfil its duty of care to protect the assets, the debtor’s duty of loyalty and duty of impartiality are relevant.
- trustees appointed where inaccuracies/inconsistencies arrive or where creditors can't trust debtor
- VOTING FOR THE PLAN
- IBC (SEC. 30)
- 66% or more
- US
- each class of impaired creditors consent to 2/3rds of volume and half of allowed claims.
- any class not impaired deemed accept plan
- any class not receiving property/claims deemed to reject plan
- UK
- proposal acceptance requires simple majority in value of creditors present & voting
- GERMANY
- approved by each creditor class
- crammed down on any non-approving class if
- plan doesn't make class worse than in case of liquidation
- creditors participate fairly in economic value distributed to creditors
- approved by majority
- FRANCE
- sauveguard proceedings-2 creditors committee plus bondholders committee
- 2/3rd approval of creditors who exercise voting rights
other various important legislations
US:US BANKRUPTCY CODE 1978











No comments:
Post a Comment